Abstract
PURPOSE Corticosteroids (2mg/kg/day) are commonly used as first-line treatment for acute graft versus host disease(aGVHD). However, steroid is effective in only about half of patients. Based on the promising efficacy of ruxolitinib as second-line therapy for aGVHD, we performed a randomized controlled study to assess the safety and efficacy of corticosteroids (2mg/kg/day) alone versus ruxolitinb combined with reduced dose of corticosteroids (1mg/kg/day) in patients with high-risk aGVHD after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation.
METHODS This multicenter, randomized, phase II controlled study (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04061876) enrolled patients with newly diagnosed aGVHD from 7 Chinese centers. Patients were randomly assigned at a ratio of 1:1 to methylprednisolone (2mg/kg/day) alone (steroids group) or ruxolitinib (5 mg/day) combined with methylprednisolone (1 mg/kg/day) (RUX/steroids combined group). The primary endpoint is the overall response rate on day 28, which is defined as an improvement of at least one stage in the severity of aGVHD in one organ without deterioration in any other organ or disappearance of any GVHD signs from all organs without requiring new systemic immunosuppressive treatment. The secondary objectives consist of response time, response duration, overall survival, disease-free survival, non-relapse mortality, failure-free survival.
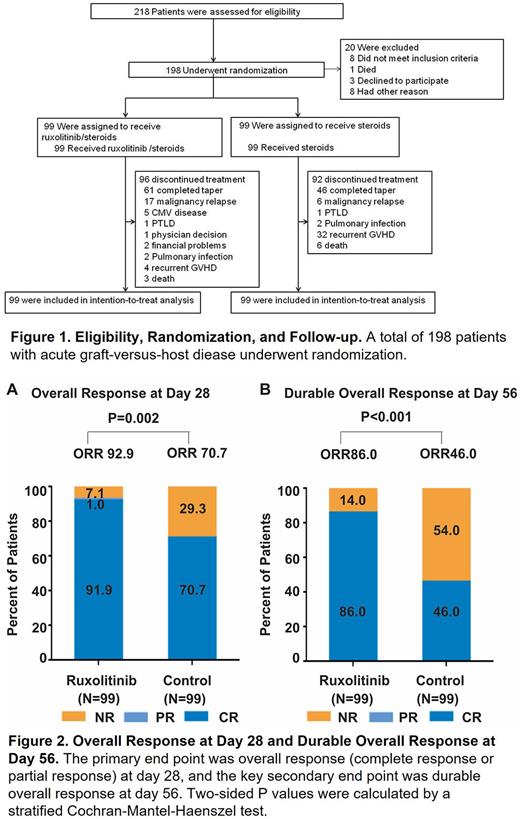
RESULTS From August 25 of 2019 to June 1 of 2022, 198 patients were enrolled and evaluated for response with a median follow-up of 601 days (Figure 1). The overall response rates at day 28 were 92.9% in the RUX/steroids combined group and 70.7% in the steroids group, respectively (P = 0.002; Figure 2A). Durable overall response at day 56 was significantly higher in the RUX/steroids combination group than in the steroids alone group (86% vs. 46%; odds ratio,7.69; P <0.001; Figure 2B) The incidences of adverse events were comparable between these two groups. For both groups, the most common grade 3 or worse adverse events were anaemia, thrombocytopenia and gamma-glutamyltransferase increased that were self-limiting.
CONCLUSION Addition of ruxolitinb (5 mg/day) to methylprednisolone (1 mg/kg/day) represents an effective first-line therapy for newly diagnosed acute GVHD, which resulted in a high overall response rate and is well tolerated. These findings are an important contribution to the field, showing a safe strategy to incorporate ruxolitinb (5 mg/d) into the standard first line regimen for newly diagnosed acute GVHD internationally.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Ruxolitinib. Based on the promising efficacy of ruxolitinib as second-line therapy for aGVHD, we performed a randomized controlled study to assess the safety and efficacy of corticosteroids (2mg/kg/day) alone versus ruxolitinb combined with reduced dose of corticosteroids (1mg/kg/day) in patients with high-risk aGVHD after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Participants began oral administration of ruxolitinib at 5 mg QD; Methylprednisolone: 1mg/kg/d , iv or iv gtt for at leas 5 days, then taper according to the clinical response.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal